What is a Hybrid?
A hybrid is a vehicle that can achieve propulsion using either a fuelled power source or stored energy.
 The fuelled power source could be:
The fuelled power source could be:
- An internal combustion engine (diesel, petrol, gas etc.)
- An external combustion engine (a Stirling Engine, steam engine etc.)
The Stored energy source may be a:
- Flywheel
- Hydraulic reservoir
- Supercapacitor
- Battery bank
Most Marine Hybrid systems use a diesel engine and a battery bank providing propulsion through an electric motor.
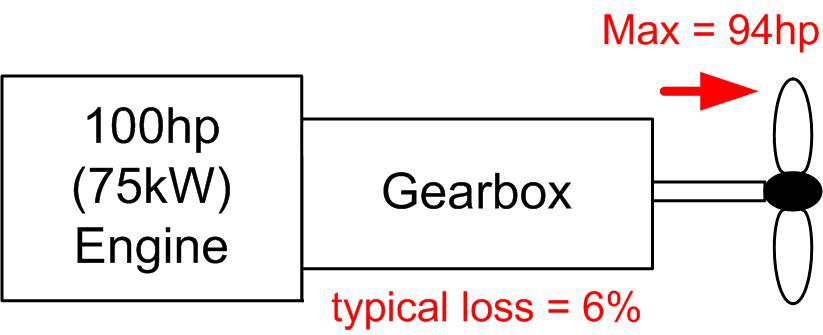
Conventional Diesel
|
Diesel Electric
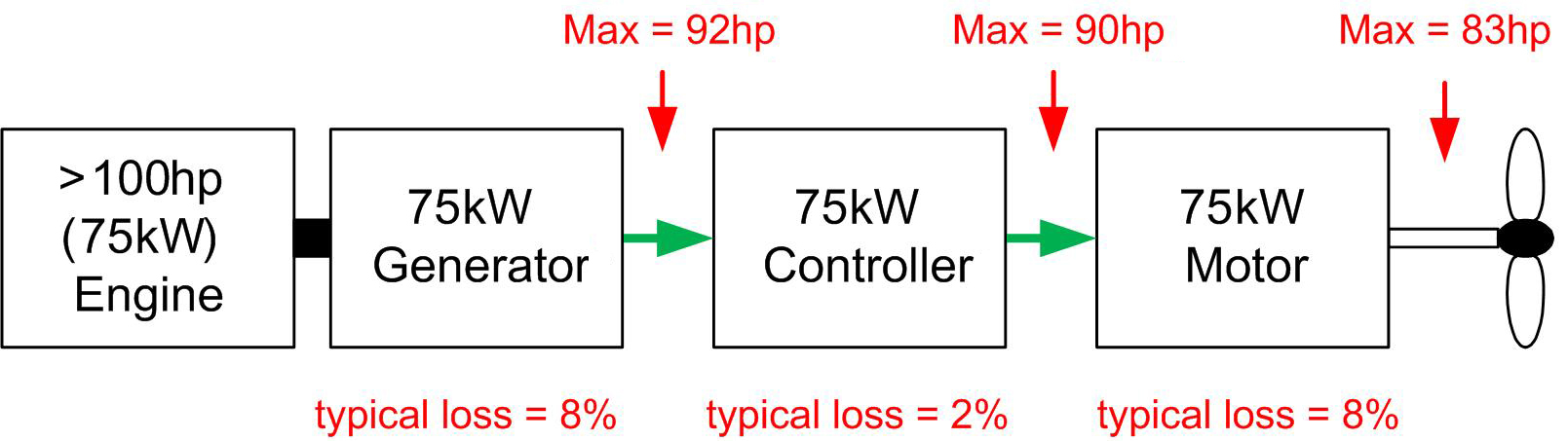
If we remove the gearbox and replace it with a generator, motor controller and motor, we now have a Diesel-Electric. The engine is mechanically coupled to the generator (usually in the same housing). From this point onwards, all power transmission is performed electrically until the motor converts the electrical energy to mechanical energy at the prop shaft. Every step in power transmission has an associated loss; some typical values are shown. Don't worry too much about understanding the losses; we will look at these more closely in a more advanced discussion.
Serial Hybrid
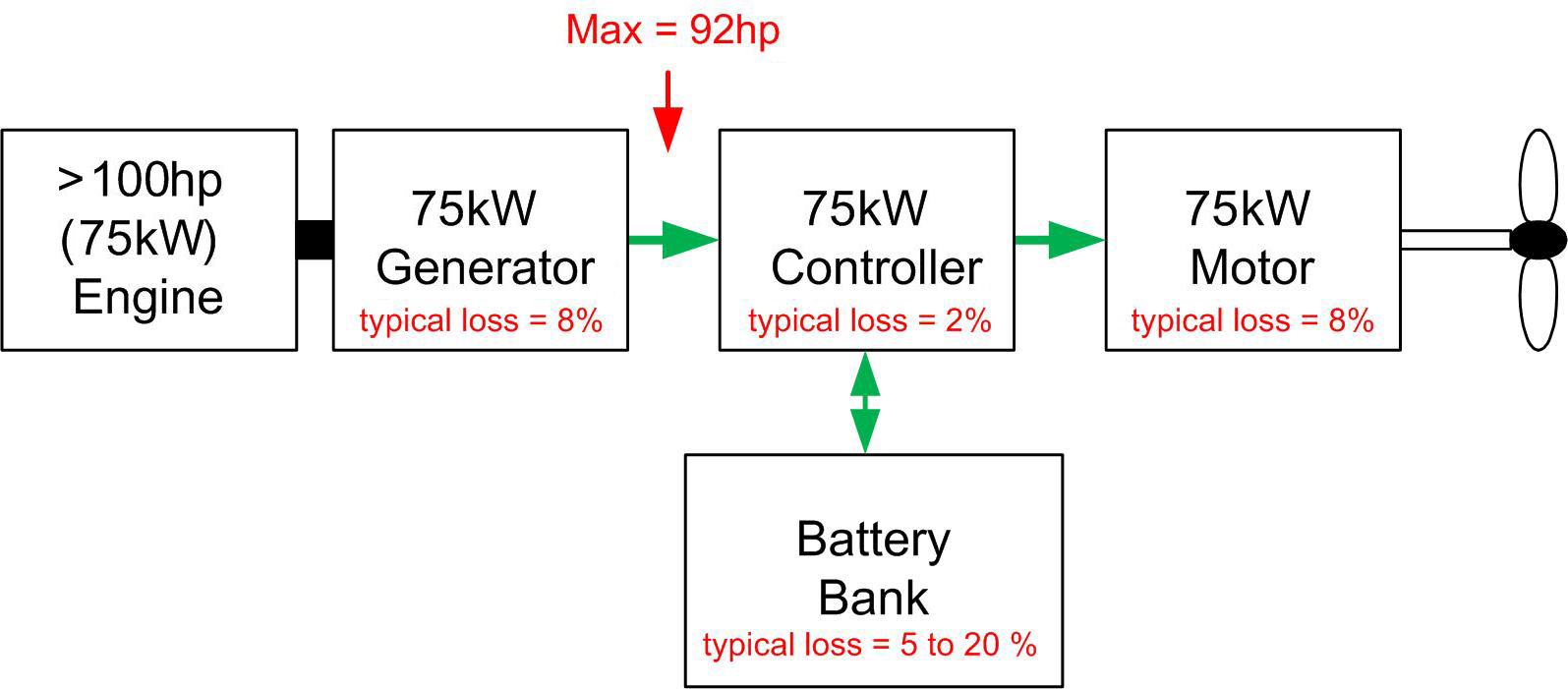
If we add a battery bank to a Diesel Electric, we have a serial Hybrid. The propeller can be driven by the engine using fuel and from the battery bank (with engine stopped) using stored energy. Typical losses are shown, these accumulate depending on the mode of operation, so again lets leave this to the more advanced discussion. The main thing to consider is that power transmission to the shaft is performed electrically, and propulsion without the engine running is possible (battery drive).
Parallel Hybrid
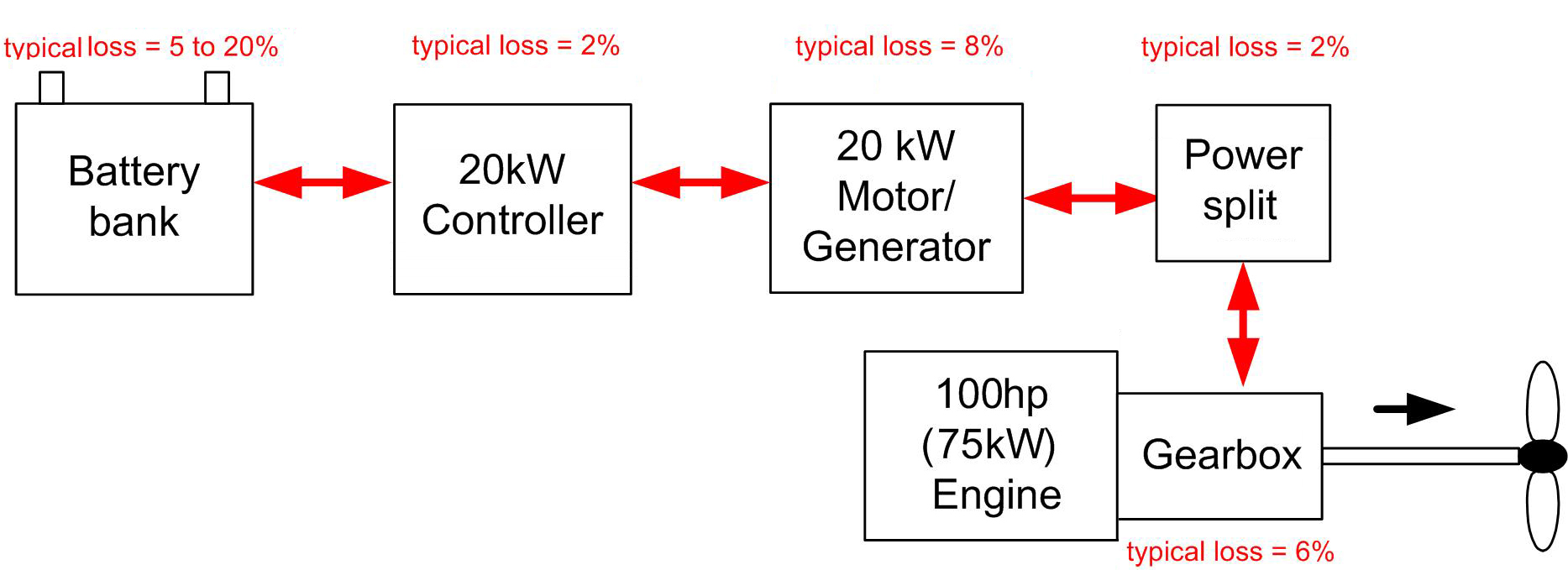
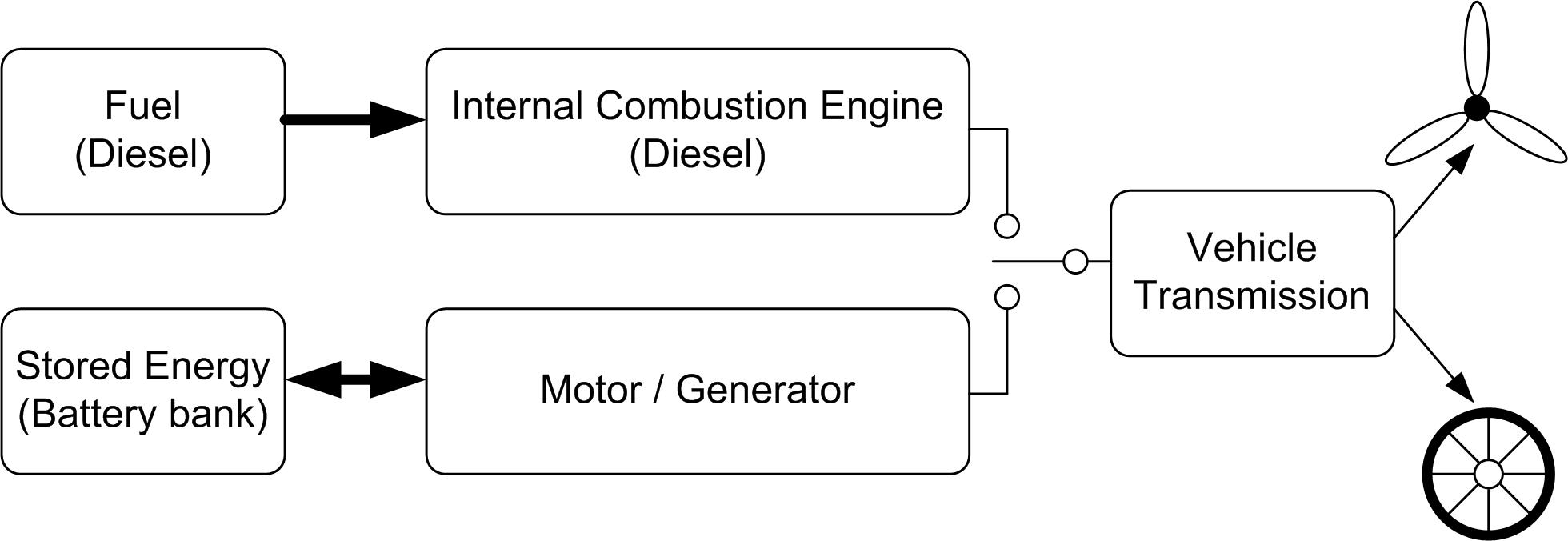
A Parallel hybrid is quite a different concept. As the name implies, two different transmission paths are connected in parallel to the prop shaft. The mechanical connection from the engine to the gearbox to the prop shaft is maintained. A separate transmission path is established from the battery bank, motor controller, and motor. A power split device is then used to connect the motor to the prop shaft; depending on the system, this may be before or after the gearbox.
Now we have established the basic Hybrid configurations, the next step is to look at the efficiencies of each system.